OPENJPA使用JPA规范
最近学习JPA,但在我们中国学习的资源还是比较少,尤其是最新的一些技术,下面我将讲讲我搭建的JPA规范的项目。
首先,创建一个项目(web或java项目都可以),然后在myeclipse里增加jpa的架包。
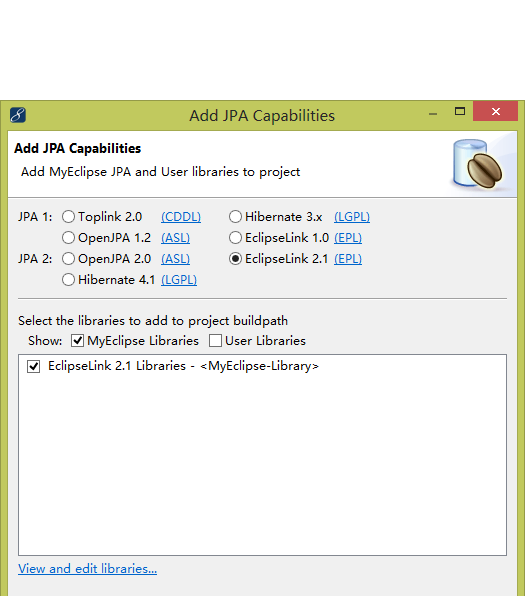
选择OpenJPA2.0
然后编写persistence.xml文件
我的文件是:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" version="2.0"><persistence-unit name="wms"><provider>org.apache.openjpa.persistence.PersistenceProviderImpl</provider><class>com.wms.jpa.model.User</class><class>com.wms.jpa.model.Message</class><properties><property name="openjpa.ConnectionDriverName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /><property name="openjpa.ConnectionURL" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost/jpawms0004?userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&createDatabaseIfNotExist=true&autoReconnect=true" /><property name="openjpa.ConnectionUserName" value="root" /><property name="openjpa.ConnectionPassword" value="2011_2015" /><!-- <property name="openjpa.Multithreaded" value="true" /><property name="openjpa.DynamicEnhancementAgent" value="false" /><property name="openjpa.RuntimeUnenhancedClasses" value="unsupported" /><property name="openjpa.ConnectionFactoryProperties" value="PrintParameters=true" /><property name="openjpa.jdbc.SynchronizeMappings" value="buildSchema(ForeignKeys=True)" /> --></properties></persistence-unit></persistence>
然后写一个实体类,每写一个实体类都要在persistence.xml里增加class.
package com.wms.jpa.model;import java.util.*;import javax.persistence.*;@Entitypublic class Message { @Id private long id = System.currentTimeMillis(); @Basic private String message; @Basic private Date created = new Date(); public Message() { } public Message(String msg) { message = msg; } public void setId(long val) { id = val; } public long getId() { return id; } public void setMessage(String msg) { message = msg; } public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setCreated(Date date) { created = date; } public Date getCreated() { return created; }}/* * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one * or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file * distributed with this work for additional information * regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file * to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the * "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance * with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, * software distributed under the License is distributed on an * "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY * KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the * specific language governing permissions and limitations * under the License. */package com.wms.jpa.test;import java.util.List;import javax.persistence.EntityManager;import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;import javax.persistence.Persistence;import javax.persistence.Query;import com.wms.jpa.model.Message;/** * A very simple, stand-alone program that stores a new entity in the * database and then performs a query to retrieve it. */public class UserTest { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a new EntityManagerFactory using the System properties. // The "hellojpa" name will be used to configure based on the // corresponding name in the META-INF/persistence.xml file EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence. createEntityManagerFactory("wms", System.getProperties()); // Create a new EntityManager from the EntityManagerFactory. The // EntityManager is the main object in the persistence API, and is // used to create, delete, and query objects, as well as access // the current transaction EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); // Begin a new local transaction so that we can persist a new entity em.getTransaction().begin(); // Create and persist a new Message entity em.persist(new Message("Hello Persistence!")); // Commit the transaction, which will cause the entity to // be stored in the database em.getTransaction().commit(); // It is always good practice to close the EntityManager so that // resources are conserved. em.close(); // Create a fresh, new EntityManager EntityManager em2 = factory.createEntityManager(); // Perform a simple query for all the Message entities Query q = em2.createQuery("select m from Message m"); // Go through each of the entities and print out each of their // messages, as well as the date on which it was created for (Message m : (List<Message>) q.getResultList()) { System.out.println(m.getMessage() + " (created on: " + m.getCreated() + ")"); } // Again, it is always good to clean up after ourselves em2.close(); factory.close(); }}然后可以看到如下的运行结果:
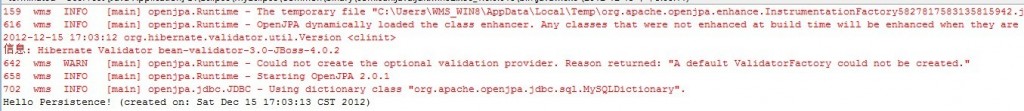
最后提醒下要导入必要的数据库驱动。
转载请注明出处http://blog.csdn.net/wu560130911/article/details/8299422