IoC容器和Dependency Injection模式
IoC与DI
首先想说说IoC(Inversion of Control,控制倒转)。这是spring的核心,贯穿始终。所谓IoC,对于spring框架来说,就是由spring来负责控制对象的生命周期和 对象间的关系。这是什么意思呢,举个简单的例子,我们是如何找女朋友的?常见的情况是,我们到处去看哪里有长得漂亮身材又好的mm,然后打听她们的兴趣爱 好、qq号、电话号、ip号、iq号………,想办法认识她们,投其所好送其所要,然后嘿嘿……这个过程是复杂深奥的,我们必须自己设计和面对每个环节。传 统的程序开发也是如此,在一个对象中,如果要使用另外的对象,就必须得到它(自己new一个,或者从JNDI中查询一个),使用完之后还要将对象销毁(比 如Connection等),对象始终会和其他的接口或类藕合起来。
那么IoC是如何做的呢?有点像通过婚介找女朋友,在我和女朋友之间引入了一个第三者:婚姻介绍所。婚介管理了很多男男女女的资料,我可以向婚 介提出一个列表,告诉它我想找个什么样的女朋友,比如长得像李嘉欣,身材像林熙雷,唱歌像周杰伦,速度像卡洛斯,技术像齐达内之类的,然后婚介就会按照我 们的要求,提供一个mm,我们只需要去和她谈恋爱、结婚就行了。简单明了,如果婚介给我们的人选不符合要求,我们就会抛出异常。整个过程不再由我自己控 制,而是有婚介这样一个类似容器的机构来控制。Spring所倡导的开发方式就是如此,所有的类都会在spring容器中登记,告诉spring你是个什 么东西,你需要什么东西,然后spring会在系统运行到适当的时候,把你要的东西主动给你,同时也把你交给其他需要你的东西。所有的类的创建、销毁都由 spring来控制,也就是说控制对象生存周期的不再是引用它的对象,而是spring。对于某个具体的对象而言,以前是它控制其他对象,现在是所有对象 都被spring控制,所以这叫控制反转。如果你还不明白的话,我决定放弃。
IoC的一个重点是在系统运行中,动态的向某个对象提供它所需要的其他对象。这一点是通过DI(Dependency Injection,依赖注入)来实现的。比如对象A需要操作数据库,以前我们总是要在A中自己编写代码来获得一个Connection对象,有了 spring我们就只需要告诉spring,A中需要一个Connection,至于这个Connection怎么构造,何时构造,A不需要知道。在系统 运行时,spring会在适当的时候制造一个Connection,然后像打针一样,注射到A当中,这样就完成了对各个对象之间关系的控制。A需要依赖 Connection才能正常运行,而这个Connection是由spring注入到A中的,依赖注入的名字就这么来的。那么DI是如何实现的呢? Java 1.3之后一个重要特征是反射(reflection),它允许程序在运行的时候动态的生成对象、执行对象的方法、改变对象的属性,spring就是通过反射来实现注入的。关于反射的相关资料请查阅java doc。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
我想通过Bromon的介绍,大家对IoC和DI都有了比较生动的理解了。再来看看《expert one-on-one J2EE Development without EJB中文版》是怎么解释这两个概念的。书上是这么说的:
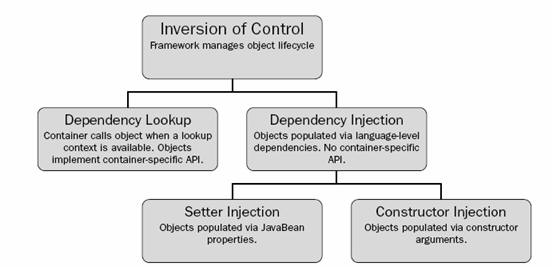
IoC是一个很大的概念,可以用不同的方式来实现。主要的实现形式有两种:
依赖查找:容器提供回调接口和上下文环境给组件。EJB和Apache Avalon都是使用这种方式。
依赖注入:组件不做定位查询,只是提供普通的Java方法让容器去决定依赖关系。容器全权负责组件的装配,它会把符合依赖关系的对象通过JavaBean属性或者构造子传递给需要的对象。通过JavaBean属性注射依赖关系的做法称为设值方法注入(Setter Injection);将依赖关系作为构造子参数传入的做法称为构造子注入(Constructor Injection)。
附图说明:
到这里,大家应该对IoC与DI都有了初步的认识了。其实就Spring来说,就是JavaBean由Spring来管理组装,表面上看就少了几个new字,其实就是为了降低耦合度,这也是我们做软件的目标之一。
至于Spring是怎样实现IoC的,《expert one-on-one J2EE Development without EJB中文版》第七章“Spring框架介绍”很详细的列举了多种方法。说实在,一下子看这么多,我真有点糊涂了。我还是自己写个Demo熟悉一下大名鼎鼎的Spring吧。
首先得下载Spring。Spring网上有两种Spring 包一种是spring-framework-1.2.6-with-dependencies.zip,另一种是spring-framework-1.2.6.zip。当然最好是下载spring-framework-1.2.6-with-dependencies.zip形式的,因为里面包括了更多的东东。spring-framework-1.2.6-with-dependencies.zip的下载地址是:http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/springframework/spring-framework-1.2.6-with-dependencies.zip。
下载下来,解压后,你会发现里面有很多jar文件。因为刚刚接触Spring,因此我只需要spring-core.jar(spring-framework-1.2.6\dist),将其导入eclipse的构建路径中。另外,log日志是需要的,这也是为了养成良好的编程习惯。将log4j-1.2.9.jar(spring-framework-1.2.6\lib\log4j)和commons-logging.jar(spring-framework-1.2.6\lib\jakarta-commons)导入到构建路径中。
准备就绪,开始写Demo了。
我的工程的结构是: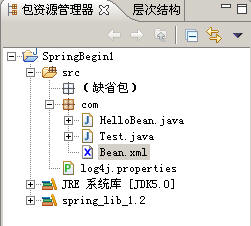
1、 log4j.properties代码:
log4j.rootLogger=Debug, stdoutlog4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppenderlog4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayoutlog4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%c{1} - %m%npackage com;public class HelloBean { private String helloworld="Hello!World!"; public String getHelloworld() { return helloworld; } public void setHelloworld(String helloworld) { this.helloworld = helloworld; }}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?><!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING/DTD BEAN/EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd"><beans> <bean id="helloBean" name="code">package com;import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //实例化JavaBean,主要是为了比较new对象和依赖注入两者的区别 HelloBean hellobean=new HelloBean(); System.out.println(hellobean.getHelloworld()); //通过Spring访问JavaBean组件 Resource resource=new ClassPathResource("com/bean.xml"); BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(resource); hellobean=(HelloBean)factory.getBean("helloBean"); System.out.println(hellobean.getHelloworld()); }}package com;public interface HelloImp { public void getName();}package com;public class Hello implements HelloImp { public void getName(){ System.out.println("Jack"); }}package com;public class HelloBean { private String helloworld="Hello!World!"; private HelloImp hello; [b]//注意这个私有对象是借口[/b] public String getHelloworld() { return helloworld; } public void setHelloworld(String helloworld) { this.helloworld = helloworld; } public void setHello(HelloImp hello) { this.hello = hello; } public void get(){ this.hello.getName(); }}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?><!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING/DTD BEAN/EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd"><beans>[b]<!—注意引用的类是具体的类Hello-->[/b] <bean id="myHello" name="code">package com;import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { HelloBean hellobean=new HelloBean(); System.out.println(hellobean.getHelloworld()); Resource resource=new ClassPathResource("com/bean.xml"); BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(resource); hellobean=(HelloBean)factory.getBean("helloBean"); System.out.println(hellobean.getHelloworld()); hellobean.get(); }}