jetty源码分析8-continuation
1.概述
jetty的continuation是用于异步处理请求,简单的讲,请求模型不再是一请求一线程,而是在请求的过程中,可以挂起当前请求,用该容器线程处理别的请求。减小请求线程数,从而减少内存占用和上下文切换。还可以使得应用对于请求更可控,比如针对不同优先级请求分别排队等。
servlet3中也有该异步请求的支持:http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/6/api/javax/servlet/AsyncContext.html
jetty相关介绍和使用文档如下:http://wiki.eclipse.org/Jetty/Feature/Continuations
以上两篇文档对于用法和为什么有比较详细的讲解,在此不赘述。
?
分析基于jetty7.2,后面版本有一些重构(比如httpconnection变成了asynchttpconnection等,但基本思想还是一样的)
?
2.结构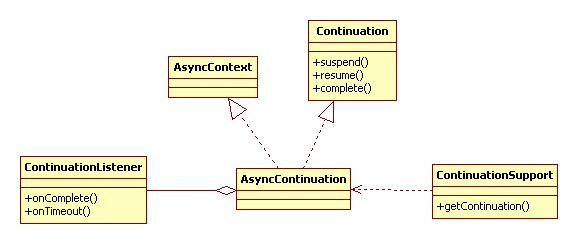
continuation有一些是支持非jetty的servelt3容器或者jetty6的类,这些都忽略掉,类图是非常简单的。
jetty7是将continuation集成到了server本身的代码中(Request的一个属性)。
protected final AsyncContinuation _async = new AsyncContinuation();
?
然后在continuationSupport中的getContinuation方法通过:
Continuation continuation = (Continuation) request.getAttribute(Continuation.ATTRIBUTE);
??
取出来。
?
?3.httpconnection的handle方法基本上,jetty的server代码和continuation已经结合到一起了,先看一下HttpConnection的handle方法
这个方法是一个非常重要的方法,也基本上算是handle线程的入口方法)SelectChannelEndPoint.handle()->HttpConnection.handle()其中SelectChannelEndPoint的handle主要是处理一些nio的事情,比如将dispatched改为false之类。
??简化后的方法代码如下:
?
public Connection handle() throws IOException { Connection connection = this; boolean more_in_buffer =true; // assume true until proven otherwise boolean progress=true; try { assert getCurrentConnection()==null; assert _handling==false; _handling=true; setCurrentConnection(this); while (more_in_buffer && _endp.isOpen()) { try { if (_request._async.isAsync()) { if (!_request._async.isComplete()) handleRequest(); else if (!_parser.isComplete()) { long parsed=_parser.parseAvailable(); progress|=parsed>0; } } else { if (!_parser.isComplete()) progress|=_parser.parseAvailable()>0; while (_generator.isCommitted() && !_generator.isComplete()) { long written=_generator.flushBuffer(); if (written<=0) break; progress=true; if (_endp.isBufferingOutput()) _endp.flush(); } if (!progress) return this; } progress=false; } catch (HttpException e) { _generator.sendError(e.getStatus(), e.getReason(), null, true); _parser.reset(true); _endp.close(); } finally { more_in_buffer = _parser.isMoreInBuffer() || _endp.isBufferingInput(); // Is this request/response round complete? if (_parser.isComplete() && _generator.isComplete() && !_endp.isBufferingOutput()) { if (!_generator.isPersistent()) { _parser.reset(true); more_in_buffer=false; _endp.close(); } reset(true); progress=true; } } } } finally { setCurrentConnection(null); _handling=false; } return connection; }??????
该方法主要分为3大块,try中的async部分,else部分,和finally部分。
?
1.async部分 (async调用一般是continuation调用了resume,complete方法走到的分支)
?
2.else部分 (正常请求的流程)
?
3. finally动作
?
4.httpconnection的handleRequest方法该方法主要有3个调用地方(不考虑delayhanding),分别是刚刚的handle方法,parser的headercomplete方法和content方法。简化后的代码方法如下
protected void handleRequest() throws IOException { try { final Server server=_server; boolean handling=_request._async.handling() && server!=null && server.isRunning(); while (handling) { _request.setHandled(false); String info=null; try { if (_request._async.isInitial()) { _request.setDispatcherType(DispatcherType.REQUEST); _connector.customize(_endp, _request); server.handle(this); } else { _request.setDispatcherType(DispatcherType.ASYNC); server.handleAsync(this); } } catch (ContinuationThrowable e) { Log.ignore(e); } finally { handling = !_request._async.unhandle() && server.isRunning() && _server!=null; } } } finally { if (_request._async.isUncompleted()) { _request._async.doComplete(); _response.complete(); _request.setHandled(true); } } }?
?有了上面的基础,我们就可以来看看AsyncContinuation 的核心,状态转移,先上图:
?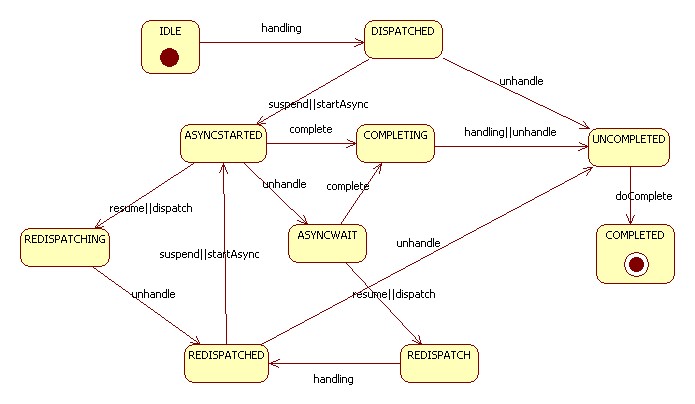
?再看一下对于每个状态的注释:
private static final int __IDLE=0; // Idle request private static final int __DISPATCHED=1; // Request dispatched to filter/servlet private static final int __ASYNCSTARTED=2; // Suspend called, but not yet returned to container private static final int __REDISPATCHING=3;// resumed while dispatched private static final int __ASYNCWAIT=4; // Suspended and parked private static final int __REDISPATCH=5; // Has been scheduled private static final int __REDISPATCHED=6; // Request redispatched to filter/servlet private static final int __COMPLETING=7; // complete while dispatched private static final int __UNCOMPLETED=8; // Request is completable private static final int __COMPLETED=9; // Request is complete
?
基本上,所有的请求都会经过这个状态转移中的一部分:
?
1.不使用continuation的是走的是IDLE--handling-->DISPATCHED---unhandle-->UNCOMPLETED--doComplete-->COMPLETED的状态转移过程,全部调用都发生在httpconnection的handlerequest方法中。
?
2.如果调用了suspend之后,会在unhandle方法中转入ASYNCWAIT,这时有两种可能从状态中转移出来,一个是超时,一个是用户显示调用resume或者complete。
?
3.在httconnection的handleRequest方法中,会调用async.handling(),handling表示请求开始处理了。这里如果是idle状态,就会转换为dispatched状态,并返回true。如果是COMPLETING状态,就转移到UNCOMPLETED状态,并返回false。如果是__ASYNCWAIT状态,就直接返回false,如果是REDISPATCH状态,就转移到REDISPATCHED,并返回true。返回false就表示不会派发给server处理。
4.在httconnection的handleRequest方法中,会调用async.unhandle()。unhandle表示一次dispath的请求结束了。这里如果是DISPATCHED状态,就会变成UNCOMPLETED,如果是ASYNCSTARTED,就转化为ASYNCWAIT(这里还有一点处理,注册超时事件)。如果是REDISPATCHING,就转化为REDISPATCHED,如果是COMPLETING,就转化为UNCOMPLETED。返回值决定是否要再走一次handleRequest的派发给server。只有状态转移为REDISPATCHED的时候,会返回false,再派发一次。
?
5.doComplete也只发生在handleRequest方法中,只有状态为UNCOMPLETED的时候会发生转移。
6.async的complete,suspend和resume都是用户调用的方法。
?
总的来说,核心的状态就是已派发(DISPATCHED),等待(ASYNCWAIT)和已完成(COMPLETED)。然后其他状态主要处理重新派发以及多线程之间的状态协调。
6.Generator的状态转移?
从前面的分析可以看到,AsyncContinuation 最终影响的是Generator的状态转移,使得在handleRequest方法中决定要不要做response.complete.(触发httpconnection.completeResponse()),在handle方法中决定要不要reset连接相关的信息。
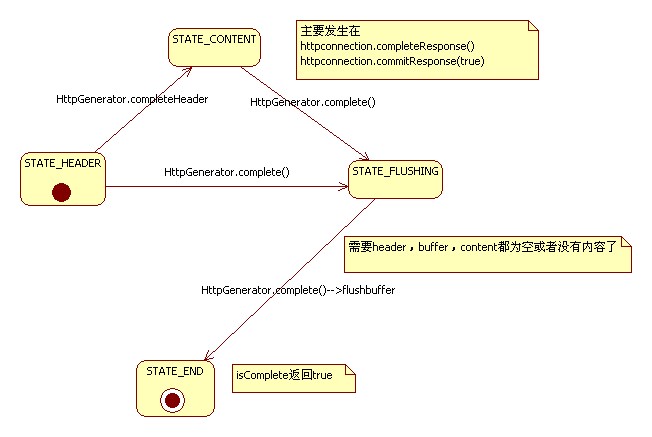
?
?
1.一旦离开了header状态,scommited就是true了
2.httpconnection.completeResponse(),httpconnection.commitResponse(boolean)是触发离开header状态的两个主要操作,
3.completeResponse只发生在一处(还有两处是senderror和sendredirect,暂时不讨论),就是千万handleRequest的finally方法中,需要async.isUncompleted的状态为uncompleted。
httpconnection.commitResponse(boolean)发生于几种情况httpconnection.output的close方法,flush方法和sendContent方法。其中flush方法的传入参数是false,就不会触发 _generator.complete();状态只能还是content,不会到FLUSHING或者END.
?
7.AsyncContinuation的几个重要操作?
1.suspend
基本上,这个方法就是创建一个AsyncEventState(用于超时判断等处理),然后将自己的state置为ASYNCSTARTED.
?
2.resume
这个方法主要是转移一下状态(上面的图),然后调用一下endpoint的dispath,重新分发一次。(把自己加入handle的线程池)
?
3.complete
? 这个方法也和resume类似,状态转移为COMPLETEING,然后调用endpoint的dispath,重新分发一次。在httpconnection的handle方法中,会走到前文async部分的分支上,然后调用handleRequest,在handleRequest的方法中调用handing方法,再转移一次状态,调用response.complete(httpconnection.responsecomplete),输出信息并结束
?
??4.timeout
?? 在unhandle方法中,会注册一个timeout事件(AsyncEventState),后台线程会轮询,发现超时就触发AsyncEventState.expired事件,改变? AsyncContinuation的状态,使得在resume,complete,dispath等方法中不再调用endpoint的dispath,同时通知所有ContinuationListener的onTimeout方法。
?
8.总结总的来说,jetty的continuation就是用了一个AsyncContinuation对象来保存处理的状态,然后在httpconnection的handle和handleRequest的方法中根据不同的状态来决定是将请求挂起等待后续处理还是关闭请求。jetty的代码总的结构非常清晰,但细节上有一些方法比较长,特别是httpparser和httpgenerator的代码,看起来有时比较麻烦,事实上还是可以重构得更易读一些。