数字集成电路设计-5-pipelining(流水线)
引言
It is quite a three-pipe problem.
-- Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
所以就分三部分说吧。
虽然,指令级并行(ILP)的潜能已经开发殆尽(intel已经在2004年宣布,停止高性能单处理器的研发),流水线技术也已经很成熟了,但是了解流水线,是学习和了解计算机体系结构绕不开的内容。本小节就从三个方面说一下流水线。
5.1 什么是流水线
Pipelining is an implementation technique whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution; it takes advantage of parallelism that exists among the actions needed to execute an instruction.
流水线是利用执行指令所需的操作之间的并行性,实现多条指令并行执行的一种技术。
其实,流水线本身,跟计算机没关系。最早流水线是福特发明的,那时福特汽车公司生产效率很低,正是福特本人引进流水线,是生产效率大增。其原理就是把生产一辆完整的汽车分成若干工序,然后从第一个零件开始,依次流过整个流水线,然后一辆完整的汽车就被生产出来了。如果你在生产工厂呆过的话,理解流水线就很容易了。我想,工厂里的生产线,应该就是所谓的流水线。
特殊的,对于计算机体系结构来说,原理和汽车流水线一样,将一条指令的完成分成若干部分(流水节拍或流水段),然后指令依次流过这些流水段,就完成了这条指令。对于经典的5级流水线,如下:
1,IF(指令取得)
需要完成的工作:
Send the program counter (PC) to memory and fetch the current instruction from memory. Update the PC to the next sequential PC by adding 4 (since each instruction is 4 bytes) to the PC.
根据PC(程序计数器)指示的地址,从存储器中取指令,并装入到IR(指令寄存器),同时PC+4。当然假设每条指令占4个字节。
2,ID(指令译码)
需要完成的工作:
Decode the instruction and read the registers corresponding to register source specifiers from the register file。
对指令进行译码,并且访问寄存器堆读出相应寄存器的内容。
3,EX(执行)
需要完成的工作:
The ALU operates on the operands prepared in the prior cycle, performing one of three functions depending on the instruction type.
Memory reference
Register-Register ALU instruction
Register-Immediate ALU instruction
ALU对上一个周期准备好的操作数进行运算,根据指令类型执行下面三种操作之一。
访问存储器
寄存器-寄存器ALU指令
寄存器-立即数ALU指令
4,MEM(访问存储器)
需要完成的工作:
If the instruction is a load, memory does a read using the effective address computed in the previous cycle. If it is a store, then the memory writes the data from the second register read from the register file using the effective address.
LOAD:从存储器中读取数据。STOR:把寄存器内容写到存储器。
5,WB(写回)
需要完成的工作:
寄存器-寄存器ALU指令,LOAD指令会经过这个流水段。
Write the result into the register file, whether it comes from the memory system (for a load) or from the ALU (for an ALU instruction).
将结果(来自LOAD指令或来自ALU)写入寄存器堆。
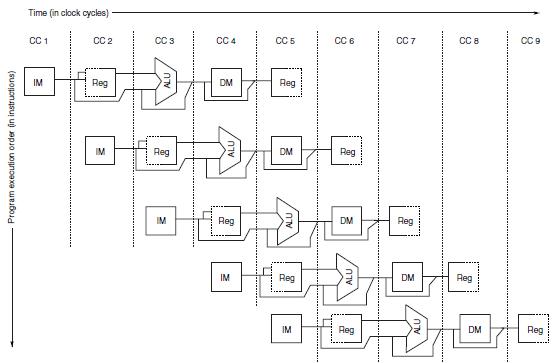
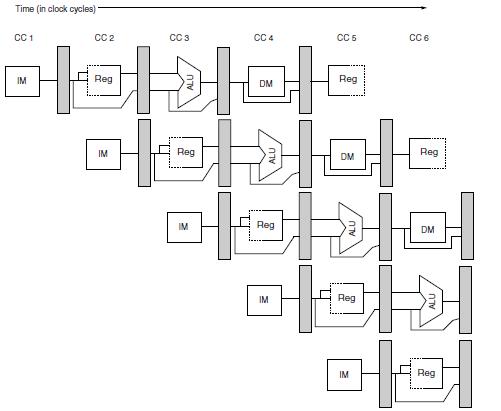
5.2流水线带来的影响
引进流水线,肯定是有好处的,会提高效率,这个先不说,天下没有完美的事,有好处就有坏处,就是会引进一些问题。哪些问题呢?如下:
1,Pipeline Hazards(流水线遇险)
1》Structural hazards(结构遇险)就是硬件资源不够用或者硬件资源使用冲突。
2》Data hazards(数据遇险)就是指令间有数据依赖关系造成的问题。
3》Control hazards(控制遇险)转移指令或修改PC造成的遇险。
2,Dealing with Exceptions(处理异常)
1》I/O中断
2》系统调用
3》执行跟踪指令
4》断点
5》定点运算溢出
6》浮点运算异常
7》页面异常
8》访问存储器时使用错误地址
9》存储保护违例
10》硬件故障
11》断电
3,Instruction Set Complications(指令集本身的复杂性)
有些体系结构的指令集用流水线实现起来就比较复杂。
这些问题,可以仔细看一下上面的两张图,好好想一下就能推断会出现这些问题,这一点很重要。
5.3 解决技术
先说一个式子:
Pipeline CPI = Ideal pipeline CPI + Structural stalls + Data hazard stalls + Control stalls
这些技术无外乎就是想方设法减小右边的4项内容其中的一项或几项。
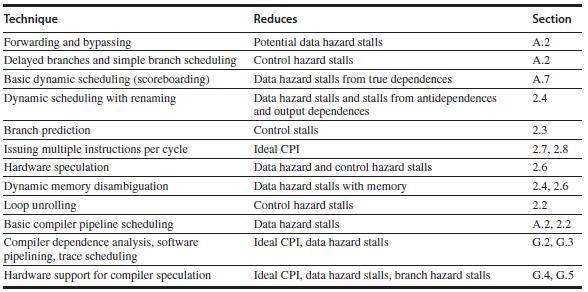
5.4小结
流水线,在各行各业都有体现,想像一下,大学食堂,如果把卖豆浆,油条,咸菜,粥,米饭,馒头,。。。这些窗口都合成一个窗口,会是什么景象。
这就是流水线的魅力。