Micro Service工具集之Swagger:可测试的样式化API文档
在我之前的一篇博文中,介绍了Yammer开发团队贡献的开源微服务开发框架DropWizard(http://ningandjiao.iteye.com/blog/1766498),有了服务之后,开发者最关心的事情是什么呢? 就是有人用你的服务。而开发者使用一个服务之前,首先需要知道的是该服务的API,目前几乎所有的开放平台都是把API以文档的形式放在网站上,如下:
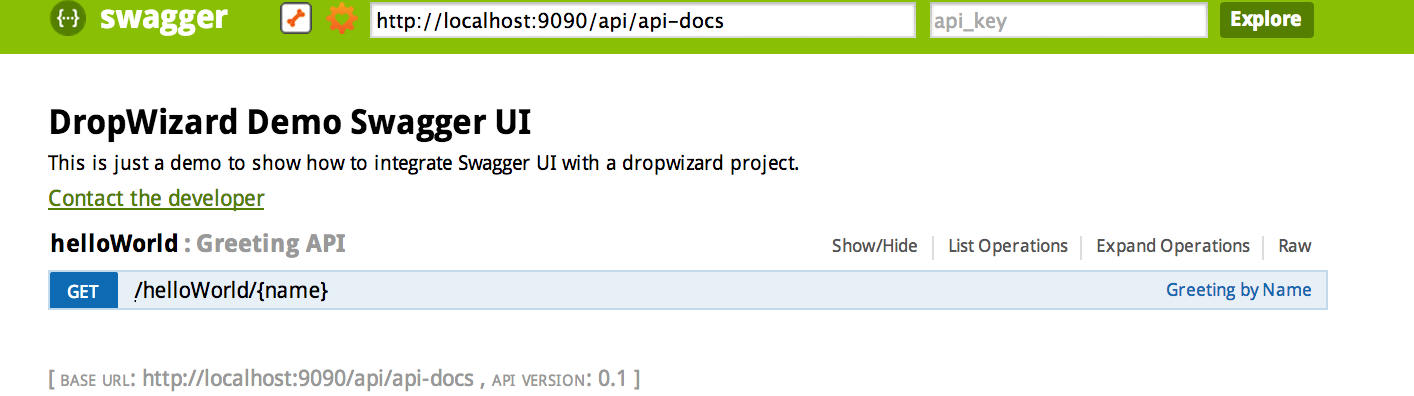
不知道有没有开发人员和我一样,有时对一些API说明的理解比较模糊,总想着能直接验证一下自己的理解就好了,而不是需要去项目写测试代码来验证自己的想法。即API文档应具备直接执行能力。 Swagger就是这样的一个利器,其实,Swagger本身的目标比上面描述的要大很多:“Swagger is a specification and complete framework implementation for describing, producing, consuming, and visualizing RESTful web services. ”。但是,本文中只想聊聊如何通过Swagger为已有项目的生成具备执行能力的样式化API文档。
为已存在的项目添加Swagger(以DropWizard为例)
首先,为项目引入Swagger依赖包
'com.wordnik:swagger-jaxrs_2.9.1:1.3.0'
private void initSwaggerConfig(Environment environment) { // Swagger Resource environment.addResource(new ApiListingResourceJSON()); // Swagger providers environment.addProvider(new ApiDeclarationProvider()); environment.addProvider(new ResourceListingProvider()); // Swagger Scanner, which finds all the resources for @Api Annotations ScannerFactory.setScanner(new DefaultJaxrsScanner()); // Add the reader, which scans the resources and extracts the resource information ClassReaders.setReader(new DefaultJaxrsApiReader()); //Config API information. this information will show on the Swagger UI page SwaggerConfig config = ConfigFactory.config(); config.setApiVersion("0.1"); config.setApiPath("/api/api-docs"); //Swagger UI 默认把API信息显示在base_path/api-docs下 config.setBasePath("http://localhost:9090/api"); config.setInfo(Option.apply(new ApiInfo("DropWizard Demo Swagger UI", "This is just a demo to show how to integrate Swagger UI with a dropwizard project.", null, "xianlinbox@gmail.com", null, null))); }@Path("/helloWorld")@Api(value = "/helloWorld", description = "Greeting API", position = 1)@Produces(APPLICATION_JSON)public class HelloWorldResource { private final String template; private final String defaultName; private final AtomicLong counter; public HelloWorldResource(String template, String defaultName) { this.template = template; this.defaultName = defaultName; this.counter = new AtomicLong(); } @GET @Path("/{name}") @ApiOperation(value = "Greeting by Name", notes = "Say hello to the people", response = SayingRepresentation.class, position = 0) @ApiResponses(value = { @ApiResponse(code = 400, message = "No Name Provided") }) @Produces(APPLICATION_JSON) @Timed public SayingRepresentation sayHello(@ApiParam(value = "name for greeting", required = true) @PathParam("name") String name) { return new SayingRepresentation(counter.incrementAndGet(), String.format(template, name != null ? name : defaultName)) ; }}@ApiModel(value = "A SayingRepresentation is a representation of greeting")@JsonSerialize(include = JsonSerialize.Inclusion.NON_NULL)public class SayingRepresentation { private long id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "greeting content", required = true) private String content; public SayingRepresentation(long id, String content) { this.id = id; this.content = content; } public long getId() { return id; } public String getContent() { return content; }}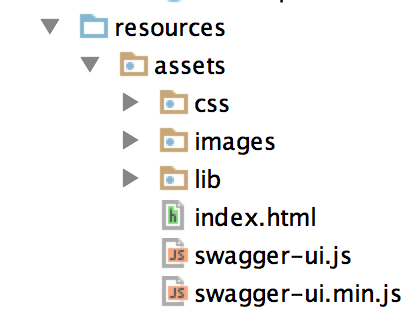
window.swaggerUi = new SwaggerUi({ url: "/api/api-docs", dom_id: "swagger-ui-container",public void initialize(Bootstrap<HelloWorldConfiguration> bootstrap) { //指定配置文件的名字 bootstrap.setName("helloWorld"); bootstrap.addBundle(new AssetsBundle("/assets", "/", "index.html")); }