Scope实现原理
内置Scope分类
Singleton 每个IOC容器对一个bean定义创建唯一实例
Prototype 对一个bean定义,每次请求容器都会创建新的实例
Request 对一个bean定义,一次web请求会创建一个实例
Session 对一个bean定义,一次web会话创建一个实例
Global Session 对一个bean定义,一次porlet会话创建一个实例
后三种只在Web环境下使用,AbstractApplicationContext refresh入口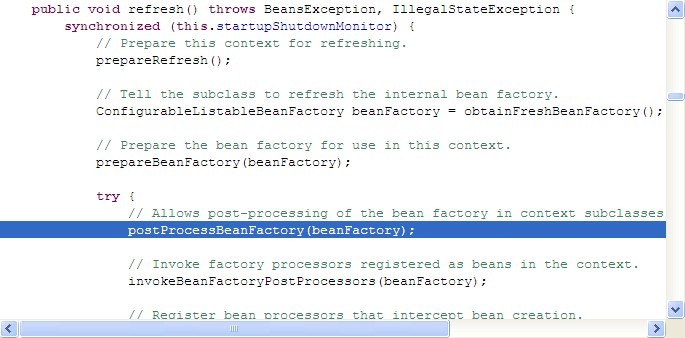
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext会注册这三种BEAN
WebApplicationContextUtils具体代码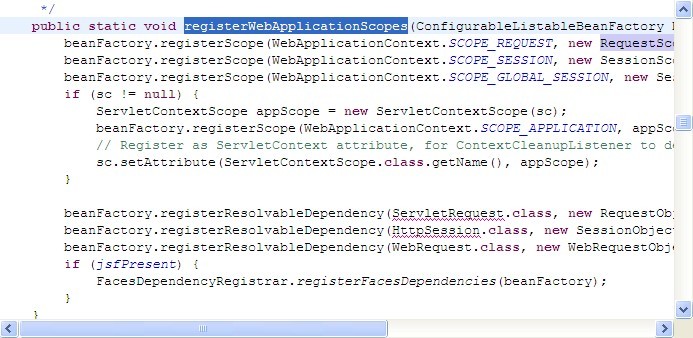
当使用AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext并不会注册这三种Bean.
这三种Scope父类方法调用RequestContextHolder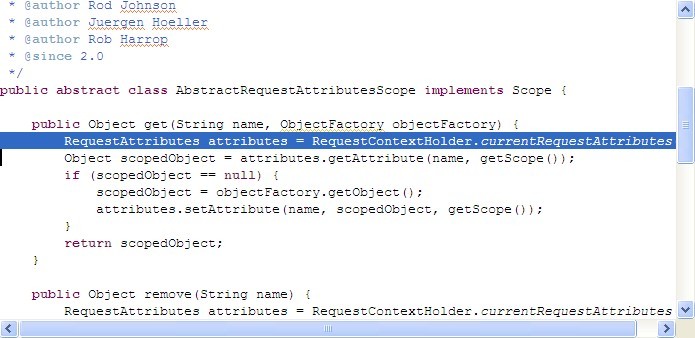
在RequestContextHolder实现中,RequestAttribute为空,则抛出错误
RequestAttribute的实现ServletRequestAttributes中,封装了HTTP对象和Scope的Bean获取,设置和销毁方法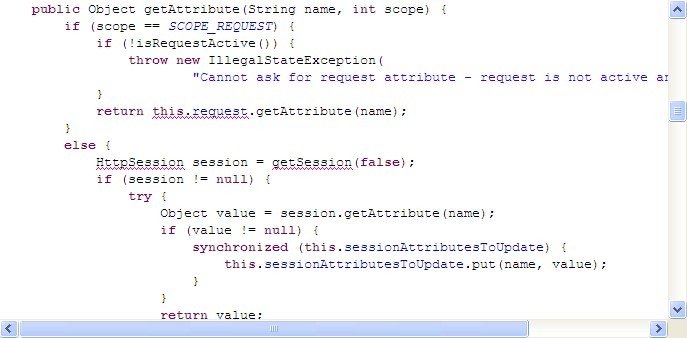

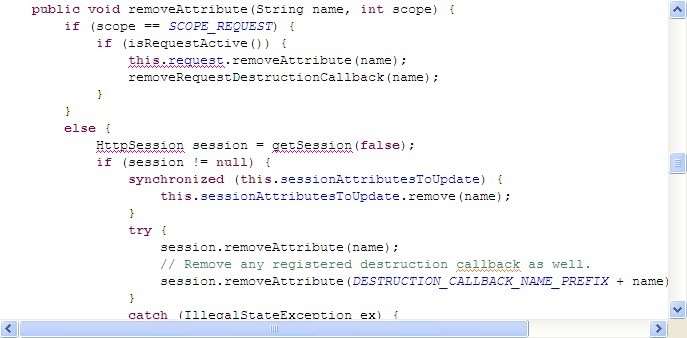
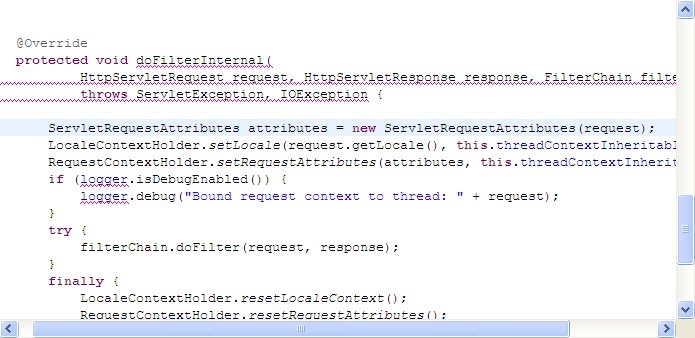
所以在WEB环境下,如果使用SPRING MVC,则在 DispatcherServlet, or DispatcherPortlet已经初始化RequestAttribute对象,否则必须做相关配置以初始化。
使用servlet2.4+容器,web.xml配置如下
<web-app>...<listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener </listener-class></listener>...</web-app>
<web-app>..<filter> <filter-name>requestContextFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.RequestContextFilter</filter-class></filter><filter-mapping> <filter-name>requestContextFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping>...</web-app>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- an HTTP Session-scoped bean exposed as a proxy --> <bean id="userPreferences" scope="session"> <!-- instructs the container to proxy the surrounding bean --> <aop:scoped-proxy/> </bean> <!-- a singleton-scoped bean injected with a proxy to the above bean --> <bean id="userService" ref="userPreferences"/> </bean></beans>
<bean id="userPreferences" scope="session"/><bean id="userManager" ref="userPreferences"/></bean>
<!-- DefaultUserPreferences implements the UserPreferences interface --><bean id="userPreferences" scope="session"> <aop:scoped-proxy proxy-target-ref="userPreferences"/></bean>
/** * Parse the elements at the root level in the document: * "import", "alias", "bean". * @param root the DOM root element of the document */protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {Node node = nl.item(i);if (node instanceof Element) {Element ele = (Element) node;if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);}else {delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);}}}}else {delegate.parseCustomElement(root);}}private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);}else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {processAliasRegistration(ele);}else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);}else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {// recursedoRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);}}

String originalBeanName = definition.getBeanName();BeanDefinition targetDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();// Create a scoped proxy definition for the original bean name,// "hiding" the target bean in an internal target definition.RootBeanDefinition proxyDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class);proxyDefinition.setOriginatingBeanDefinition(definition.getBeanDefinition());proxyDefinition.setSource(definition.getSource());proxyDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);String targetBeanName = getTargetBeanName(originalBeanName);proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", targetBeanName);if (proxyTargetClass) {targetDefinition.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);// ScopedFactoryBean's "proxyTargetClass" default is TRUE, so we don't need to set it explicitly here.}else {proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.FALSE);}// Copy autowire settings from original bean definition.proxyDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(targetDefinition.isAutowireCandidate());proxyDefinition.setPrimary(targetDefinition.isPrimary());if (targetDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {proxyDefinition.copyQualifiersFrom((AbstractBeanDefinition) targetDefinition);}// The target bean should be ignored in favor of the scoped proxy.targetDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(false);targetDefinition.setPrimary(false);// Register the target bean as separate bean in the factory.registry.registerBeanDefinition(targetBeanName, targetDefinition);// Return the scoped proxy definition as primary bean definition// (potentially an inner bean).return new BeanDefinitionHolder(proxyDefinition, originalBeanName, definition.getAliases());/* * Copyright 2002-2009 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */package org.springframework.aop.scope;import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;import org.springframework.aop.framework.AopInfrastructureBean;import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyConfig;import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;import org.springframework.aop.support.DelegatingIntroductionInterceptor;import org.springframework.aop.target.SimpleBeanTargetSource;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBeanNotInitializedException;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;/** * Convenient proxy factory bean for scoped objects. * * <p>Proxies created using this factory bean are thread-safe singletons * and may be injected into shared objects, with transparent scoping behavior. * * <p>Proxies returned by this class implement the {@link ScopedObject} interface. * This presently allows for removing the corresponding object from the scope, * seamlessly creating a new instance in the scope on next access. * * <p>Please note that the proxies created by this factory are * <i>class-based</i> proxies by default. This can be customized * through switching the "proxyTargetClass" property to "false". * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 2.0 * @see #setProxyTargetClass */public class ScopedProxyFactoryBean extends ProxyConfig implements FactoryBean<Object>, BeanFactoryAware {/** The TargetSource that manages scoping */private final SimpleBeanTargetSource scopedTargetSource = new SimpleBeanTargetSource();/** The name of the target bean */private String targetBeanName;/** The cached singleton proxy */private Object proxy;/** * Create a new ScopedProxyFactoryBean instance. */public ScopedProxyFactoryBean() {setProxyTargetClass(true);}/** * Set the name of the bean that is to be scoped. */public void setTargetBeanName(String targetBeanName) {this.targetBeanName = targetBeanName;this.scopedTargetSource.setTargetBeanName(targetBeanName);}public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {if (!(beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory)) {throw new IllegalStateException("Not running in a ConfigurableBeanFactory: " + beanFactory);}ConfigurableBeanFactory cbf = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) beanFactory;this.scopedTargetSource.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();pf.copyFrom(this);pf.setTargetSource(this.scopedTargetSource);Class beanType = beanFactory.getType(this.targetBeanName);if (beanType == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot create scoped proxy for bean '" + this.targetBeanName +"': Target type could not be determined at the time of proxy creation.");}if (!isProxyTargetClass() || beanType.isInterface() || Modifier.isPrivate(beanType.getModifiers())) {pf.setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanType, cbf.getBeanClassLoader()));}// Add an introduction that implements only the methods on ScopedObject.ScopedObject scopedObject = new DefaultScopedObject(cbf, this.scopedTargetSource.getTargetBeanName());pf.addAdvice(new DelegatingIntroductionInterceptor(scopedObject));// Add the AopInfrastructureBean marker to indicate that the scoped proxy// itself is not subject to auto-proxying! Only its target bean is.pf.addInterface(AopInfrastructureBean.class);this.proxy = pf.getProxy(cbf.getBeanClassLoader());}public Object getObject() {if (this.proxy == null) {throw new FactoryBeanNotInitializedException();}return this.proxy;}public Class<?> getObjectType() {if (this.proxy != null) {return this.proxy.getClass();}if (this.scopedTargetSource != null) {return this.scopedTargetSource.getTargetClass();}return null;}public boolean isSingleton() {return true;}}Scope threadScope = new SimpleThreadScope();beanFactory.registerScope("thread", threadScope);<bean id="..." scope="thread">
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean scope="thread"> <property name="name" value="Rick"/> <aop:scoped-proxy/> </bean> <bean id="foo" ref="bar"/> </bean></beans>
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {if (this.scopes != null) {for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : this.scopes.entrySet()) {String scopeKey = entry.getKey();Object value = entry.getValue();if (value instanceof Scope) {beanFactory.registerScope(scopeKey, (Scope) value);}else if (value instanceof Class) {Class scopeClass = (Class) value;Assert.isAssignable(Scope.class, scopeClass);beanFactory.registerScope(scopeKey, (Scope) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(scopeClass));}else if (value instanceof String) {Class scopeClass = ClassUtils.resolveClassName((String) value, this.beanClassLoader);Assert.isAssignable(Scope.class, scopeClass);beanFactory.registerScope(scopeKey, (Scope) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(scopeClass));}else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mapped value [" + value + "] for scope key [" +scopeKey + "] is not an instance of required type [" + Scope.class.getName() +"] or a corresponding Class or String value indicating a Scope implementation");}}}}/** * Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans, * respecting explicit order if given. * <p>Must be called before singleton instantiation. */protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryPostProcessors =new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()) {if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryPostProcessor =(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;registryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);registryPostProcessors.add(registryPostProcessor);}else {regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);}}Map<String, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> beanMap =beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryPostProcessorBeans =new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>(beanMap.values());OrderComparator.sort(registryPostProcessorBeans);for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : registryPostProcessorBeans) {postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);}invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryPostProcessors, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryPostProcessorBeans, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);processedBeans.addAll(beanMap.keySet());}else {// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(getBeanFactoryPostProcessors(), beanFactory);}// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!String[] postProcessorNames =beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,// Ordered, and the rest.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {// skip - already processed in first phase above}else if (isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}else if (isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}else {nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}}// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.OrderComparator.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {orderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}OrderComparator.sort(orderedPostProcessors);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);}