【转】Struts2的工作机制及分析-2
查找静态资源的源代码如清单14:
?
代码清单14:FilterDispatcher.findStaticResource()方法
??? protected void findStaticResource(String name, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
??????? if (!name.endsWith(".class")) {//忽略class文件
?????????? //遍历packages参数
??????????? for (String pathPrefix : pathPrefixes) {
??????????????? InputStream is = findInputStream(name, pathPrefix);//读取请求文件流
??????????????? if (is != null) {
??????????????????? ……(省略部分代码)
??????????????? ??? // set the content-type header
??????????????????? String contentType = getContentType(name);//读取内容类型
??????????????????? if (contentType != null) {
??????????????????????? response.setContentType(contentType);//重新设置内容类型
??????????????????? }
????????????????? ……(省略部分代码)
??????????????????? try {
???????????????????? //将读取到的文件流以每次复制4096个字节的方式循环输出
??????????????????????? copy(is, response.getOutputStream());
??????????????????? } finally {
??????????????????????? is.close();
??? ????????????????}
??????????????????? return;
??????????????? }
??????????? }
??????? }
??? }
?
??? 如果用户请求的资源不是以/struts开头——可能是.jsp文件,也可能是.html文件,则通过过滤器链继续往下传送,直到到达请求的资源为止。
?
??? 如果getMapping()方法返回有效的ActionMapping对象,则被认为正在请求某个Action,将调用Dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping)方法,该方法是处理Action的关键所在。上述过程的源代码如清单15所示。
?
代码清单15:FilterDispatcher.doFilter()方法
??? public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
??????? HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
??????? HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
??????? ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
??????? String timerKey = "FilterDispatcher_doFilter: ";
??????? try {
??????????? UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
??????????? request = prepareDispatcherAndWrapRequest(request, response);//重新包装request
??????????? ActionMapping mapping;
??????????? try {
??????????????? mapping = actionMapper.getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());//得到存储Action信息的ActionMapping对象
??????????? } catch (Exception ex) {
?????????????? ……(省略部分代码)
??????????????? return;
??????????? }
?
??????????? if (mapping == null) {//如果mapping为null,则认为不是请求Action资源
???????????????? String resourcePath = RequestUtils.getServletPath(request);
?
??????????????? if ("".equals(resourcePath) && null != request.getPathInfo()) {
??????????????????? resourcePath = request.getPathInfo();
??????????????? }
????????????? //如果请求的资源以/struts开头,则当作静态资源处理
??????????????? if (serveStatic && resourcePath.startsWith("/struts")) {
??????????????????? String name = resourcePath.substring("/struts".length());
??????????????????? findStaticResource(name, request, response);
??????????????? } else {
??????????????????? //否则,过滤器链继续往下传递
??????????????????? chain.doFilter(request, response);
??????????????? }
??????????????? // The framework did its job here
??????????????? return;
??????????? }
?????????? //如果请求的资源是Action,则调用serviceAction方法。
??????????? dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
?
??????? } finally {
??????????? try {
??????????????? ActionContextCleanUp.cleanUp(req);
??????????? } finally {
??????????????? UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
??????????? }
??????? }
??? }
???
??? 这段代码的活动图如图18所示: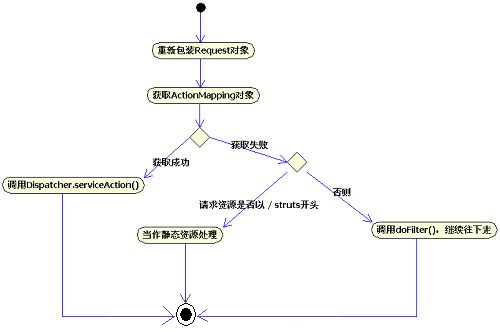
?
(图18)
?
??? 在Dispatcher.serviceAction()方法中,先加载Struts2的配置文件,如果没有人为配置,则默认加载struts-default.xml、struts-plugin.xml和struts.xml,并且将配置信息保存在形如com.opensymphony.xwork2.config.entities.XxxxConfig的类中。
?
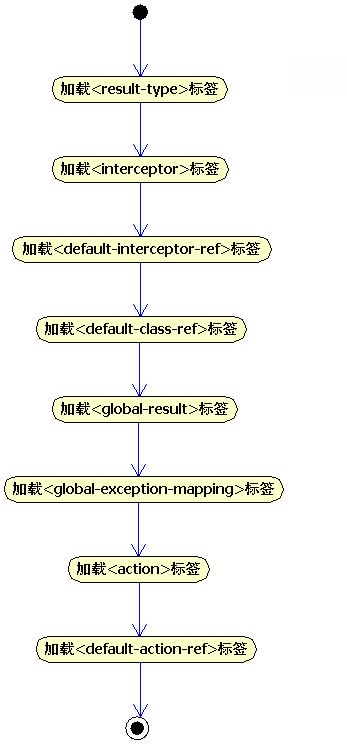
??? 类com.opensymphony.xwork2.config.providers.XmlConfigurationProvider负责配置文件的读取和解析, addAction()方法负责读取<action>标签,并将数据保存在ActionConfig中;addResultTypes()方法负责将<result-type>标签转化为ResultTypeConfig对象;loadInterceptors()方法负责将<interceptor>标签转化为InterceptorConfi对象;loadInterceptorStack()方法负责将<interceptor-ref>标签转化为InterceptorStackConfig对象;loadInterceptorStacks()方法负责将<interceptor-stack>标签转化成InterceptorStackConfig对象。而上面的方法最终会被addPackage()方法调用,将所读取到的数据汇集到PackageConfig对象中,细节请参考代码清单16。
?
代码清单16:XmlConfigurationProvider.addPackage()方法
??? protected PackageConfig addPackage(Element packageElement) throws ConfigurationException {
??????? PackageConfig newPackage = buildPackageContext(packageElement);
??????? if (newPackage.isNeedsRefresh()) {
??????????? return newPackage;
??????? }
??????? if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
??????????? LOG.debug("Loaded " + newPackage);
??????? }
??????? // add result types (and default result) to this package
??????? addResultTypes(newPackage, packageElement);
??????? // load the interceptors and interceptor stacks for this package
??????? loadInterceptors(newPackage, packageElement);
??????? // load the default interceptor reference for this package
??????? loadDefaultInterceptorRef(newPackage, packageElement);
??????? // load the default class ref for this package
??????? loadDefaultClassRef(newPackage, packageElement);
??????? // load the global result list for this package
??????? loadGlobalResults(newPackage, packageElement);
??????? // load the global exception handler list for this package
??????? loadGlobalExceptionMappings(newPackage, packageElement);
??????? // get actions
??????? NodeList actionList = packageElement.getElementsByTagName("action");
??????? for (int i = 0; i < actionList.getLength(); i++) {
??????????? Element actionElement = (Element) actionList.item(i);
??????????? addAction(actionElement, newPackage);
??????? }
??????? // load the default action reference for this package
??????? loadDefaultActionRef(newPackage, packageElement);
???? ???configuration.addPackageConfig(newPackage.getName(), newPackage);
??????? return newPackage;
??? }
???
??? 活动图如图19所示:
?
(图19)
??? 配置信息加载完成后,创建一个Action的代理对象——ActionProxy引用,实际上对Action的调用正是通过ActionProxy实现的,而ActionProxy又由ActionProxyFactory创建,ActionProxyFactory是创建ActionProxy的工厂。
?
注:ActionProxy和ActionProxyFactory都是接口,他们的默认实现类分别是DefaultActionProxy和DefaultActionProxyFactory,位于com.opensymphony.xwork2包下。
?
??? 在这里,我们绝对有必要介绍一下com.opensymphony.xwork2.DefaultActionInvocation类,该类是对ActionInvocation接口的默认实现,负责Action和截拦器的执行。
?
??? 在DefaultActionInvocation类中,定义了invoke()方法,该方法实现了截拦器的递归调用和执行Action的execute()方法。其中,递归调用截拦器的代码如清单17所示:
代码清单17:调用截拦器,DefaultActionInvocation.invoke()方法的部分代码
?? ??? if (interceptors.hasNext()) {
????????????? //从截拦器集合中取出当前的截拦器
??? ?????????? final InterceptorMapping interceptor = (InterceptorMapping) interceptors.next();
??? ?????????? UtilTimerStack.profile("interceptor: "+interceptor.getName(),
??? ????????????????? new UtilTimerStack.ProfilingBlock<String>() {
???????????????????????? public String doProfiling() throws Exception {
??????????????????????????? //执行截拦器(Interceptor)接口中定义的intercept方法
????????????? ??? ?????????? resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
????????????? ??? ?????????? return null;
???????????????????????? }
??? ?????????? });
??? ?????? }
?
??? 从代码中似乎看不到截拦器的递归调用,其实是否递归完全取决于程序员对程序的控制,先来看一下Interceptor接口的定义:
?
代码清单18:Interceptor.java
public interface Interceptor extends Serializable {
??? void destroy();
??? void init();
??? String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception;
}
?
??? 所有的截拦器必须实现intercept方法,而该方法的参数恰恰又是ActionInvocation,所以,如果在intercept方法中调用invocation.invoke(),代码清单17会再次执行,从Action的Intercepor列表中找到下一个截拦器,依此递归。下面是一个自定义截拦器示例:
?
代码清单19:CustomIntercepter.java
public class CustomIntercepter extends AbstractInterceptor {
??? @Override
??? public String intercept(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) throws Exception
??? {
?????? actionInvocation.invoke();
?????? return "李赞红";
??? }
}
?
??? 截拦器的调用活动图如图20所示: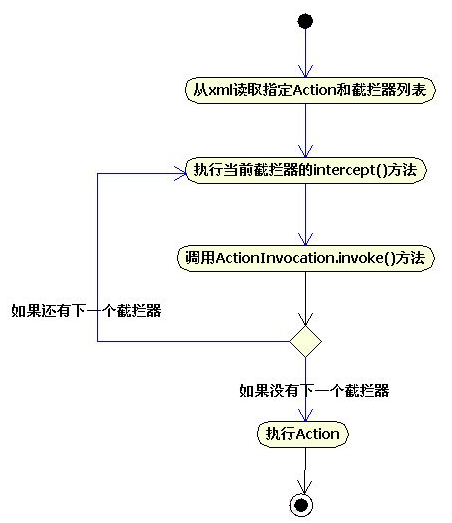
?
(图20)
?
??? 如果截拦器全部执行完毕,则调用invokeActionOnly()方法执行Action,invokeActionOnly()方法基本没做什么工作,只调用了invokeAction()方法。
?
??? 为了执行Action,必须先创建该对象,该工作在DefaultActionInvocation的构造方法中调用init()方法早早完成。调用过程是:DefaultActionInvocation()->init()->createAction()。创建Action的代码如下:
?
代码清单20:DefaultActionInvocation.createAction()方法
??? protected void createAction(Map contextMap) {
??????? try {
??????????? action = objectFactory.buildAction(proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getNamespace(), proxy.getConfig(), contextMap);
??????? } catch (InstantiationException e) {
?????? ……异常代码省略
??????? }
??? }
?
??? Action创建好后,轮到invokeAction()大显身手了,该方法比较长,但关键语句实在很少,用心点看不会很难。
?
代码清单20:DefaultActionInvocation.invokeAction()方法
protected String invokeAction(Object action, ActionConfig actionConfig) throws Exception {
??? //获取Action中定义的execute()方法名称,实际上该方法是可以随便定义的
??????? String methodName = proxy.getMethod();
??????? String timerKey = "invokeAction: "+proxy.getActionName();
??????? try {
??????????? UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);???????????
??? ????????Method method;
??????????? try {
????????????? //将方法名转化成Method对象
??????????????? method = getAction().getClass().getMethod(methodName, new Class[0]);
??????????? } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
??????????????? // hmm -- OK, try doXxx instead
??????????? ????try {
????????????????? //如果Method出错,则尝试在方法名前加do,再转成Method对象
??????????????????? String altMethodName = "do" + methodName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + methodName.substring(1);
??????????????????? method = getAction().getClass().getMethod(altMethodName, new Class[0]);
??????????????? } catch (NoSuchMethodException e1) {
??????????????????? // throw the original one
??????????????????? throw e;
??????????????? }
??????????? }
?????????? //执行方法
??????????? Object methodResult = method.invoke(action, new Object[0]);
??????? ????//处理跳转
??? ??? if (methodResult instanceof Result) {
??????????? ??? this.result = (Result) methodResult;
??????????? ??? return null;
??????????? } else {
??????????? ??? return (String) methodResult;
??????????? }
??????? } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
????????????? ……省略异常代码
??????? } finally {
??????????? UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
??????? }
??? }
?
??? 刚才使用了一段插述,我们继续回到ActionProxy类。
?
??? 我们说Action的调用是通过ActionProxy实现的,其实就是调用了ActionProxy.execute()方法,而该方法又调用了ActionInvocation.invoke()方法。归根到底,最后调用的是DefaultActionInvocation.invokeAction()方法。
?
??? 以下是调用关系图:
???
??? 其中:
????????? ActionProxy:管理Action的生命周期,它是设置和执行Action的起始点。
????????? ActionInvocation:在ActionProxy层之下,它表示了Action的执行状态。它持有Action实例和所有的Interceptor
?
??? 以下是serviceAction()方法的定义:
?
代码清单21:Dispatcher.serviceAction()方法
??? ??? public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context,
????????????????????????????? ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
??????? Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
?
??? ????// If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action
??????? ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
??????? if (stack != null) {
????????? ??extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, ValueStackFactory.getFactory().createValueStack(stack));
??????? }
?
??????? String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
??????? try {
??????????? UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
??????????? String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
??????????? String name = mapping.getName();
??????????? String method = mapping.getMethod();
?
??????????? Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
??????????? ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
??????????????????? namespace, name, extraContext, true, false);
??????????? proxy.setMethod(method);
??????????? request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
?
??????????? // if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
??????????? if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
??????????????? Result result = mapping.getResult();
??????????????? result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
??????? ????} else {
??????????????? proxy.execute();
??????????? }
?
??????????? // If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request
??????????? if (stack != null) {
??????????????? request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
??????????? }
??????? } catch (ConfigurationException e) {
??????????? LOG.error("Could not find action or result", e);
??????????? sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
??????? } catch (Exception e) {
??? ????????throw new ServletException(e);
??????? } finally {
??????????? UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
??????? }
??? }
?
??? 最后,通过Result完成页面的跳转。
?
3.4 本小节总结
?????? 总体来讲,Struts2的工作机制比Struts1.x要复杂很多,但我们不得不佩服Struts和WebWork开发小组的功底,代码如此优雅,甚至能够感受看到两个开发小组心神相通的默契。两个字:佩服。
?