ibatis源码学习(五)缓存设计和实现
缓存不算是ibatis框架的一个亮点,但理解ibatis的缓存设计和实现对我们合理使用ibatis缓存是很有帮助的。本文将深入分析ibatis框架的缓存设计和实现。缓存的使用参见官方文档:Cache Models。本文使用的ibatis版本为2.3.4。
问题
在介绍ibatis缓存设计和实现之前,我们先思考几个问题。
1. 缓存的目标是什么? 缓存中存放哪些数据?
2. 缓存数据的生命周期是怎样? 何时创建? 何时更新? 何时清理?
3. 缓存数据的作用域是怎样? Session? 应用范围?
4. 有哪些缓存管理策略? 如何加载策略配置? 如何使用这些策略?
5. 缓存key的生成由哪些因素决定?
如果你能轻松回答上面这些问题,恭喜,你没有继续看下去的必要了 ,本文将围绕这些问题分析ibatis缓存的设计和实现。
,本文将围绕这些问题分析ibatis缓存的设计和实现。
核心类图
缓存相关的核心如下: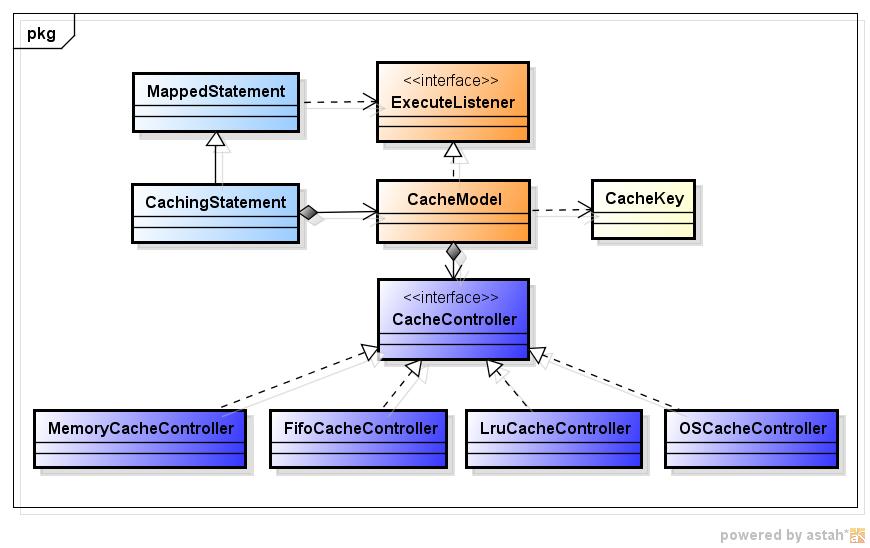
1. CacheModel
ibatis缓存的核心类,代表一个缓存对象,内部包含该缓存的配置信息(刷新间隔、缓存管理策略等)。该类和配置文件中的<cacheModel>标签对应。每个CacheModel内部组合一个CacheController对象,用于维护缓存数据。
2. CacheController
该接口表示采用某种策略的缓存管理者,缓存数据实际维护在CacheController实现类中。ibatis框架默认提供了四种缓存管理策略:MemoryCacheController提供了基于reference类型的管理策略;FifoCacheController提供了"先进先出"方式的管理策略;LruCacheController提供了"近期最少使用"的管理策略;OSCacheController提供了基于OSCache2.0缓存的管理策略。每种策略的实现方式将在下文介绍。
3. ExecuteListener
该接口表示一个观察者,它的唯一实现类是CacheModel。将该观察者注册到某个MappedStatement对象中,目的是当MappedStatement执行时,通知ExecuteListener执行相应操作(清除缓存对象)。该接口用于实现<flushOnExecute>这个功能。
4. MappedStatement
该类表示sql语句信息和执行时相关上下文环境。其内部包含List属性executeListeners,表示在sql执行后需要通知的观察者列表。
5. CachingStatement
该类是MappedStatement的包装类,用于sql执行时增加缓存功能。在配置文件中指定cacheModel属性的sql statement初始化时都会被包装成该对象。
示例
下面以常见的ibaits缓存配置举例,说明缓存的实现过程。
<cacheModel id="CATEGORY-CACHE" type="Memory" serialize="false" readOnly="true"> <property name="reference-type" value="WEAK" /> <flushInterval minutes="15" /> <flushOnExecute statement="MS-UPDATE-CATEGORY" /> </cacheModel> <select id="MS-FIND-SUB-CATEGORY" resultMap="RM-PF-PIC-CATEGORY" parameter cacheModel="CATEGORY-CACHE"> select id,cat_name,parent_id,is_leaf,prohibit_flag from PF_PIC_CATEGORY where parent_id=#parentId# </select> <update id="MS-UPDATE-CATEGORY" parametername="code">public class SqlMapParser { private void addCacheModelNodelets() { parser.addNodelet("/sqlMap/cacheModel", new Nodelet() { public void process(Node node) throws Exception { Properties attributes = NodeletUtils.parseAttributes(node, state.getGlobalProps()); //解析各属性值 String id = state.applyNamespace(attributes.getProperty("id")); String type = attributes.getProperty("type"); String readOnlyAttr = attributes.getProperty("readOnly"); Boolean readOnly = readOnlyAttr == null || readOnlyAttr.length() <= 0 ? null : new Boolean("true".equals(readOnlyAttr)); String serializeAttr = attributes.getProperty("serialize"); ... // 生成CacheModelConfig对象 CacheModelConfig cacheConfig = state.getConfig().newCacheModelConfig(id, (CacheController) Resources.instantiate(clazz), readOnly.booleanValue(), serialize.booleanValue()); state.setCacheConfig(cacheConfig); } }); ... }}public class SqlStatementParser { public void parseGeneralStatement(Node node, MappedStatement statement) { ... String cacheModelName = state.applyNamespace(attributes.getProperty("cacheModel")); ... //下面这段代码在MappedStatementConfig的构造方法中,这里为了方便说明 if (cacheModelName != null && cacheModelName.length() > 0 && client.getDelegate().isCacheModelsEnabled()) { //获取上面生成的cacheModel对象 CacheModel cacheModel = client.getDelegate().getCacheModel(cacheModelName); //生成包装者对象 mappedStatement = new CachingStatement(statement, cacheModel); } else { mappedStatement = statement; } ... }}public class SqlMapConfiguration{ private void wireUpCacheModels() { // 循环处理每一个cacheModel Iterator cacheNames = client.getDelegate().getCacheModelNames(); while (cacheNames.hasNext()) { String cacheName = (String) cacheNames.next(); CacheModel cacheModel = client.getDelegate().getCacheModel(cacheName); //获取cacheModel对应的flushTriggerStatement,由<flushOnExecute>配置 Iterator statementNames = cacheModel.getFlushTriggerStatementNames(); while (statementNames.hasNext()) { String statementName = (String) statementNames.next(); MappedStatement statement = client.getDelegate().getMappedStatement(statementName); if (statement != null) { //注册观察者 statement.addExecuteListener(cacheModel); } else { throw new RuntimeException("Could not find statement named '" + statementName + "' for use as a flush trigger for the cache model named '" + cacheName + "'."); } } ... } }} public Object executeQueryForObject(StatementScope statementScope, Transaction trans, Object parameterObject, Object resultObject) throws SQLException { //获取CacheKey CacheKey cacheKey = getCacheKey(statementScope, parameterObject); cacheKey.update("executeQueryForObject"); //根据cacheKey查询缓存value Object object = cacheModel.getObject(cacheKey); if (object == CacheModel.NULL_OBJECT){ //已缓存,值为null object = null; }else if (object == null) { //没有缓存,通过组合的statement查询 object = statement.executeQueryForObject(statementScope, trans, parameterObject, resultObject); //将查询结果放入缓存中 cacheModel.putObject(cacheKey, object); } return object; } public Object getObject(CacheKey key) { Object value = null; synchronized (this) { // 判断缓存对象有没有过期,如果过期则清除 if (flushInterval != NO_FLUSH_INTERVAL && System.currentTimeMillis() - lastFlush > flushInterval) { flush(); } // 通过controller查询缓存value value = controller.getObject(this, key); // 如果设置readOnly=false, serialize=true,需要反序列化缓存value if (serialize && !readOnly && (value != NULL_OBJECT && value != null)) { try { ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream((byte[]) value); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis); value = ois.readObject(); ois.close(); } catch (Exception e) { ... } } ... return value; } public void putObject(CacheKey key, Object value) { if (null == value) value = NULL_OBJECT; synchronized ( this ) { // 如果设置readOnly=false, serialize=true,需要序列化缓存value if (serialize && !readOnly && value != NULL_OBJECT) { try { ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); oos.writeObject(value); oos.flush(); oos.close(); value = bos.toByteArray(); } catch (IOException e) { ... } } // 通过controller更新缓存 controller.putObject(this, key, value); ... } } public class MemoryCacheController implements CacheController { private MemoryCacheLevel cacheLevel = MemoryCacheLevel.WEAK; private Map cache = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap()); public void putObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key, Object value) { Object reference = null; //弱引用 if (cacheLevel.equals(MemoryCacheLevel.WEAK)) { reference = new WeakReference(value); //软应用 } else if (cacheLevel.equals(MemoryCacheLevel.SOFT)) { reference = new SoftReference(value); //强引用 } else if (cacheLevel.equals(MemoryCacheLevel.STRONG)) { reference = new StrongReference(value); } cache.put(key, reference); } public Object getObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key) { Object value = null; Object ref = cache.get(key); if (ref != null) { if (ref instanceof StrongReference) { value = ((StrongReference) ref).get(); } else if (ref instanceof SoftReference) { value = ((SoftReference) ref).get(); } else if (ref instanceof WeakReference) { value = ((WeakReference) ref).get(); } } return value; }}public class FifoCacheController implements CacheController { private int cacheSize; // 缓存大小 private Map cache; // 缓存实际存储对象 private List keyList; //链表,用于控制key顺序 public void putObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key, Object value) { cache.put(key, value); keyList.add(key); // 超过缓存最大值的处理策略 if (keyList.size() > cacheSize) { try { //清除最先进来的key Object oldestKey = keyList.remove(0); cache.remove(oldestKey); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { ... } } } public Object getObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key) { return cache.get(key); }}public class LruCacheController implements CacheController { private int cacheSize; // 缓存大小 private Map cache; // 缓存实际存储对象 private List keyList; //链表,用于控制key顺序 public void putObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key, Object value) { cache.put(key, value); keyList.add(key); if (keyList.size() > cacheSize) { try { Object oldestKey = keyList.remove(0); cache.remove(oldestKey); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //ignore } } } public Object getObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key) { Object result = cache.get(key); // 每次查询后,将key移到List的尾部 keyList.remove(key); if (result != null) { keyList.add(key); } return result; }}public class OSCacheController implements CacheController { private static final GeneralCacheAdministrator CACHE = new GeneralCacheAdministrator(); public Object getObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key) { String keyString = key.toString(); try { int refreshPeriod = (int) (cacheModel.getFlushIntervalSeconds()); return CACHE.getFromCache(keyString, refreshPeriod); } catch (NeedsRefreshException e) { CACHE.cancelUpdate(keyString); return null; } } public void putObject(CacheModel cacheModel, Object key, Object object) { String keyString = key.toString(); CACHE.putInCache(keyString, object, new String[]{cacheModel.getId()}); }} public CacheKey getCacheKey(StatementScope statementScope, Object parameterObject) { //生成CacheKey CacheKey key = statement.getCacheKey(statementScope, parameterObject); if (!cacheModel.isReadOnly() && !cacheModel.isSerialize()) { //更新CacheKey key.update(statementScope.getSession()); } return key; } public CacheKey getCacheKey(StatementScope statementScope, Object parameterObject) { Sql sql = statementScope.getSql(); ParameterMap pmap = sql.getParameterMap(statementScope, parameterObject); CacheKey cacheKey = pmap.getCacheKey(statementScope, parameterObject); cacheKey.update(id); cacheKey.update(baseCacheKey); cacheKey.update(sql.getSql(statementScope, parameterObject)); return cacheKey; }