总结Spring Security
总结Spring Security之 关于Authentication
?
前言
开始花了两三天的时间学Spring Security,还是云山雾罩的,大受打击。于是重新总结一下,飞越迷雾,梳理思路,写这样一篇文字。网上有个雷锋写了Spring Security2 学习精讲:http://www.javaeye.com/topic/319965里面包含可以运行的代码,如果你对spring scurity感兴趣,可以快速浏览一下下面的笔记,然后debug code,然后再看看笔记。Spring Security的内容远比笔记复杂,我只是根据自己的理解挑重要的记录并整理一下。把sample code也当作笔记的一部分,那个code还是比较精简地,更重要的是实用。
官方提供的sample code包居然没有源代码,faint, google半天找到http://grepcode.com/snapshot/repo1.maven.org/maven2/org.springframework.security/spring-security-samples-contacts/2.0.0 当然,如果你会用git的话也可以自己check out code, 不过我没用过git这种高级货。
正文
跟权限有关的两个概念是 认证 和 授权, 先上个图:
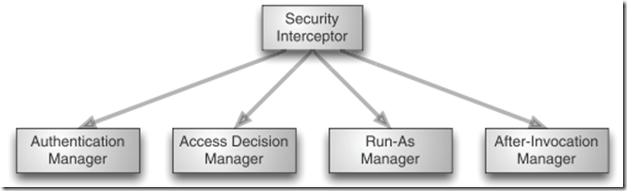
Run-As Manager 和 After-Invocation Manager不重要
The? actual? implementation? of? a? security? interceptor? will? depend? on? what resource is being secured. If you’re securing a URL in a web application, the security? interceptor? will? be? implemented? as? a? servlet? filter.? But? if? you’re? securing? a method invocation, aspects will be used to enforce security.
这篇只说Authentication Manager:
认证是通过AuthenticationManager来管的,
public interface AuthenticationManager {
? public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
????? throws AuthenticationException;
}
The? authenticate()? method? will? attempt? to? authenticate? the? user? using? the org.acegisecurity.Authentication object (which carries the principal and credentials). If successful, the authenticate() method returns a complete Authentication? object,? including? information? about? the? user’s? granted? authorities (which will be considered by the authorization manager).
具体的工作是交给各个 authentication provider来做的:
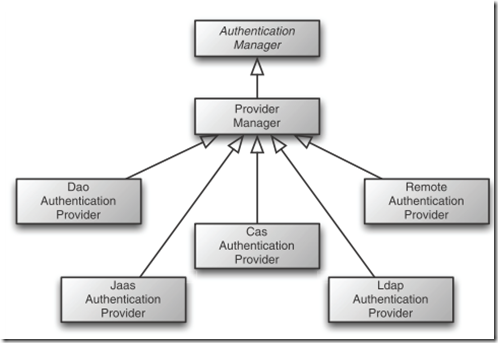
这里provider manager包含多个具体的providers:
<bean id="authenticationManager"?
??? class="org.acegisecurity.providers.ProviderManager">
? <property name="providers">
??? <list>
????? <ref bean="daoAuthenticationProvider"/>
????? <ref bean="ldapAuthenticationProvider"/>
??? </list>
? </property>
</bean>
ProviderManager is given its list of authentication providers through its providers property.
以DaoAuthenticationProvider举例:
<bean id="authenticationProvider"?
??? class="org.acegisecurity.providers.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider">
? <property name="userDetailsService"
????? ref="userDetailsService"/>
</bean>
它会要求一个UserDetailsService, 跟它相关的是UserDetails接口
UserDetailsService接口是个简单的接口
public interface UserDetailsService {
??? UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException, DataAccessException;
}
?
UserDetails接口如下:
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
??? GrantedAuthority[] getAuthorities();
??? String getPassword();
??? String getUsername();
??? boolean isAccountNonExpired();
??? boolean isAccountNonLocked();
??? boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
??? boolean isEnabled();
}
解释一下getAuthorities:该方法返回一个GrantedAuthority[]数组对象,GrantedAuthority是用户权限信息对象,这个对象中定义了一个获取用户权限描述信息的getAuthority()方法。
需要注意Authentication对象才是Spring Security使用的进行安全访问控制用户信息安全对象。实际上,Authentication对象有未认证和已认证两种状态,在作为参数传入认证管理器(AuthenticationManager)的authenticate方法时,是一个未认证的对象,它从客户端获取用户的身份信息(如用户名,密码),可以是从一个登录页面,也可以从Cookie中获取,并由系统自动构造成一个Authentication对象。而这里提到的UserDetails代表一个用户安全信息的源(从数据库,LDAP服务器,CA中心返回),Spring Security要做的就是将这个未认证的Authentication对象和UserDetails进行匹配,成功后将UserDetails中的用户权限信息拷贝到Authentication中组成一个完整的Authentication对象,共其它组件共享。
?
总结Spring Security之 关于授权,保护web和保护方法
?
* 关于授权
AcessDecisionManager是管授权的。具体授权(authorization)的工作是交给一系列Voter来做的。每个Voter都实现AccessDecisionVoter接口的vote方法,返回?
int ACCESS_GRANTED = 1;(投赞成票)
int ACCESS_ABSTAIN = 0;(投弃权票)
int ACCESS_DENIED = -1; (投反对票)
AccessDecisioinManager有三种实现:
AffirmativeBased -当至少有一个投票者投允许访问票时允许访问
ConsensusBased - 当所有投票者都投允许访问票时允许访问
UnanimousBased - 当没有投票者投拒绝访问票时允许访问
Spring Security提供了一个实用的voter:
RoleVoter participates in a vote when the secured resource has a configuration attribute whose name starts with ROLE_.
*? 关于保护web
Spring Security提供一套filter chain保护web应用
注意FilterToBeanProxy
<filter>?
? <filter-name>Spring Security Filter Chain Proxy</filter-name>?
? <filter-class>org.acegisecurity.util.FilterToBeanProxy</filter-class>?
? <init-param>?
??? <param-name>targetClass</param-name>?
??? <param-value>org.acegisecurity.util.FilterChainProxy</param-value>?
? </init-param>?
</filter>
跑下题,说FilterToBeanProxy的作用:filter配置在web.xml里,它是不可能有IOC的概念的,服务没办法自动注射到filter中,这时候有一个办法就是使用WebApplicationContextUtils(如WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext).getBean("securityManager"))。按照SpringSide的说法,WebApplicationContextUtils适合厨房,卫生间,草坪,屋顶等非常规场所,汗…这么做的一个缺点是,Spring的API还是入侵到你的code里了(向来对Rod Johnson的入侵论不感冒,感觉这纯是顺手拽过来揍EJB的板砖,不值得深究,pojo粉丝估计要拍我板砖了,俺穿个软猬甲先。入侵论深入人心之后,大家反而愿意对Spring的偶尔入侵指指点点。另外不喜欢Spring的两个方面是,从DDD的角度看Spring不natural;contract first我觉得是扯淡的,或许在之后的博客乱喷一下我的看法)解决入侵的方法就是FilterToBeanProxy, 它把真正的工作代理给target class,而spring拿到target class的类名后,就归它管了。 proxy是个简单的模式,但用在这里感觉还是挺巧妙的。
回到正题,filter chain里至少包括四个filter:
Integration Filter - 拿之前的authentication, 通常是从session里拿。
AuthenticationProcessing Filter - 处理authentication request, 比如登录的时候
Exception Translation Filter - 典型的处理是,把AuthenticationException转登录页,把AccessNeniedException转403错误页
Filter Security Interceptor - 它是真正做权限处理的,把AuthenticaionManager 和AccessDecisionManager串起来.所以FilterSecurityInterceptor是重点。
先看一个配置示例:
1: <beans:bean id="resourceSecurityInterceptor" class="org.springframework.security.intercept.web.FilterSecurityInterceptor">
2: <beans:property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager"/>
3: <beans:property name="accessDecisionManager" ref="accessDecisionManager"/>
4: <beans:property name="objectDefinitionSource" ref="secureResourceFilterInvocationDefinitionSource" />
5: <beans:property name="observeOncePerRequest" value="false" />
6: <custom-filter after="LAST" />
7: </beans:bean>
这里objectDefinitionSource属性来定义受保护的资源,保护web的时候,“资源”代表url. 保护method的时候,资源就代表method, 关于保护method之后再讨论。【有取舍地引用 spring security学习总结】首先让我们来认识一下系统为我们提供的 ObjectDefinitionSource接口,objectDefinitionSource属性正是指向此接口的实现类。其中有个重要方法,ConfigAttributeDefinition getAttributes(Object object)方法用户获取保护资源对应的权限信息,该方法返回一个ConfigAttributeDefinition对象,该对象中实际就只有一个List列表,我们可以通过使用 ConfigAttributeDefinition类的构造函数来创建这个List列表,这样,安全拦截器就通过调用 getAttributes(Object object)方法来获取ConfigAttributeDefinition对象,并将该对象和当前用户拥有的Authentication对象传递给 accessDecisionManager,accessDecisionManager再将其传递给voter们,这些投票者从ConfigAttributeDefinition对象中获取这个存放了访问保护资源需要的权限信息的列表,然后遍历这个列表并与Authentication对象中GrantedAuthority[]数据中的用户权限信息进行匹配,如果匹配成功,投票者就会投赞成票,否则就投反对票,最后accessDecisionManager来统计这些投票决定用户是否能访问该资源。【有取舍地引用 spring security学习总结结束】如果你用的是role voter的话,那么返回的ConfigAttributeDefinition其实就是一系列Role_XXX
?
说到这里小结一下之前说的认证,授权和"保护web”,涉及三个概念,user, role, resource. 认证的过程是鉴定你的身份,并且顺便把role也关联上。user和role是多对多的。 授权是处理role和resource之间的关系的,也是多对多。典型的resource是servlet URL路径。从实战的角度讲,authentication需要我们自己做的有两个事情:一是通过实现UserService.loadUserByUsername(String userName)完成认证的本职工作;二是通过实现Users.getAuthorities()把user和role关联起来。
?
* 保护方法:
Spring提供了两种方式保护方法,一种是AOP,另一种是annotation.
AOP:
如果你已经看懂了上面关于objectDefinitionSource的介绍和小结部分,那么直接看配置应该很容易可以看懂:
1:?
2: <bean id="autoProxyCreator"
3: class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator">
4:
5: <property name="interceptorNames">
6:
7: <list>
8:
9: <value>securityInterceptor</value>
10:
11: </list>
12: </property>
13: <property
14: name="beanNames">
15:
16: <list>
17:
18: <value>courseService</value>
19:
20: <value>billingService</value>
21:
22: </list>
23: </property>
24: </bean>
25:?
26: <bean id="securityInterceptor"
27:
28: class="org.acegisecurity.intercept.method.MethodSecurityInterceptor">
29:
30: <property name="authenticationManager">
31: <ref
32: bean="authenticationManager"/>
33: </property>
34:
35: <property name="accessDecisionManager">
36: <ref
37: bean="accessDecisionManager"/>
38: </property>
39:
40: <property name="objectDefinitionSource">
41:
42: <value>
43:
44: com.springinaction.springtraining.service.CourseService.createCourse=ROLE_ADMIN
45:
46: com.springinaction.springtraining.service.CourseService.enroll*=ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_REGISTRAR
47:
48: </value>
49: </property>
50: </bean>
?
注意上面的倒数几行定义了方法和对应的role
annotation:
最终目标是通过这种方式定义权限
?
1: /**
2: * @@org.acegisecurity.SecurityConfig("ROLE_ADMIN") 3: * @@org.acegisecurity.SecurityConfig("ROLE_REGISTRAR")4: */
5: public void enrollStudentInCourse(Course course, Student student) throws CourseException;
这个看起来很酷,但是有个drawback是,如果你做的是产品,并且允许用户灵活配置role和method(capability)的功能,那么annotation就不适用了,因为annotation是写死在code里的,compile time已经把role和method之间的map写死了。
这个没啥理论逻辑可谈,直接贴spring in action的配置:
1:?
2: <bean
3: id="attributes"class="org.springframework.metadata.commons.CommonsAttributes"/>
4:?
5: <bean id="objectDefinitionSource"
6: class="org.acegisecurity.intercept.method.MethodDefinitionAttributes">
7:
8: <property name="attributes"><ref
9: bean="attributes"/></property>
10: </bean>
11:?
12: <bean id="securityInterceptor"
13:
14: class="org.acegisecurity.intercept.method.MethodSecurityInterceptor">
15: …
16:
17: <property name="objectDefinitionSource">
18: <ref
19: bean="objectDefinitionSource"/>
20:
21: </property>
22: </bean>